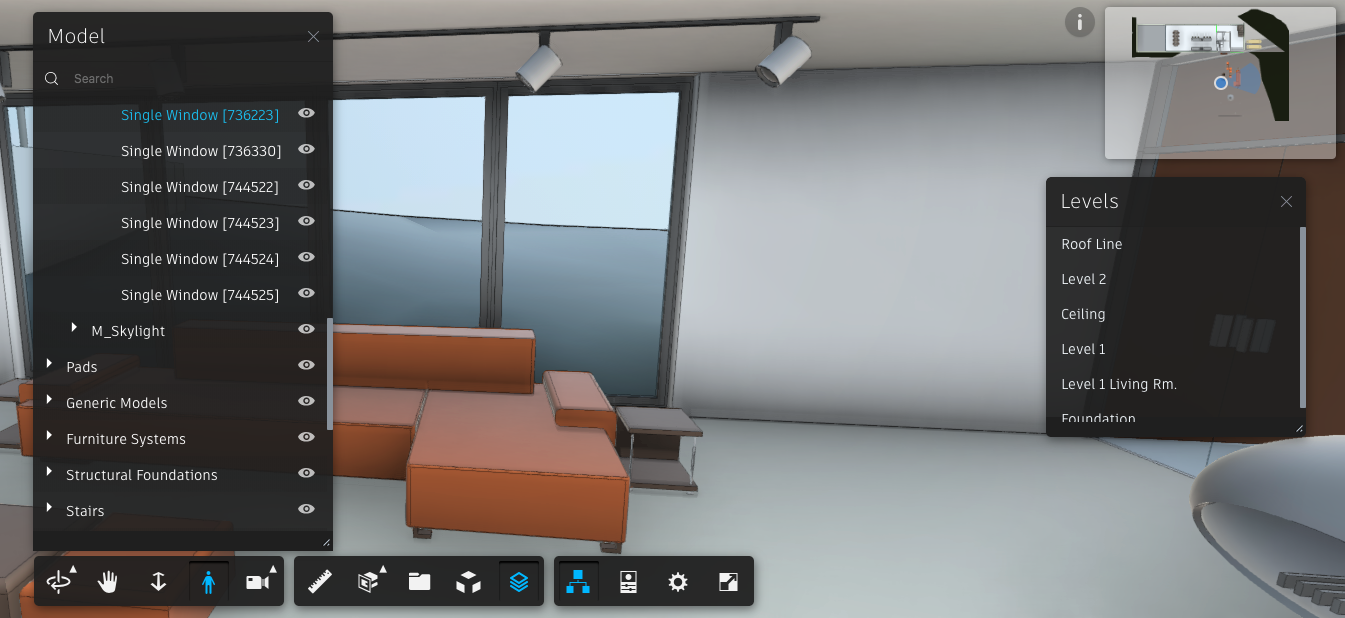
Consume AEC data with SVFs on your own server
Recently we had quite a few inquiries about how to consume the AEC data on Viewer, but that apparently involves loading the model from Forge with Viewer.loadDocumentNode. Many developers have since been wondering if it’s possible to repeat the same feat with models/SVFs downloaded to their own storage - today this will be our quest! (If you missed our instructions to consume AEC data, Michael, Kevin and Xiaodong summed it up pretty well here)
Live demo: https://jsbin.com/cuzewum/edit?js
Disclaimer: the approach to initialize and load Viewer document arbitrarily described herein is not officially supported and the validity of relevant sample code is subject to change without prior notice - use with caution at your own risk.
Indeed, with the release of v7 comes a real need to find a way to load SVFs from our own server with loadDocumentNode by their URLs, since a few other features that come with v7 rely on that as well, e.g. the Document Browser. So let’s get down to business right away. First let’s initialize a Viewer’s Document without loading it by its URN from Forge - basically a document is nothing but a representation of the derivative manifest so let’s simply pass in the manifest as JSON object to initialize it, so our code changes from:
const options = {
env: 'AutodeskProduction'
//...
}
Autodesk.Viewing.Initializer(options, () => {
Autodesk.Viewing.Document.load(urn, viewerDocument => {
Viewer.loadDocumentNode(viewerDocument, geometry)
}
})
To:
const options = {
env: 'Local'
//...
}
Autodesk.Viewing.Initializer(options, () => {
const viewerDocument = new Autodesk.Viewing.Document(manifestJsonObject) //Populate the manifest object by querying the manifest endpoint
Viewer.loadDocumentNode(viewerDocument, geometry)
//...
})
You must have noticed that Autodesk.Viewing.Document.load is but a static helper to load the manifest from Forge into a document object. And if you lost track of your model’s URN or your manifest you can upload the model to Forge and extract again and query the manifest, since you will need to do so to extract the AEC data anyway.
Then organize your SVFs in the same directory structure as they are on Forge, say the URN of my SVF is
urn%3Aadsk.viewing%3Afs.file%3AdXJuOmFkc2sub2JqZWN0czpvcy5vYmplY3Q6c2JzYjIzMzMvc2JhaGFoYWhhaGEucnZ0%2Foutput%2FResource%2F3D_View%2F_3D_%20168550%2F_3D_.svf
then we should decode this path and put the SVF and all other resources in ‘pathtomodel3D_View_3D_ 168550/3D.svf ’ on our server and keep the other resources in the same relative paths.
Now here comes the thing: although we initialized the environment as “Local” Viewer would still attempt to prefix the SVF path with Forge’s endpoint paths, these endpoint path values are not overridable with setEndpointAndApi that we usually used to override the Forge host names unfortunately … We hence need to override the method to compose the derivative URLs instead:
Autodesk.Viewing.endpoint.getItemApi=(endpoint, derivativeUrn, api)=>{
return '/path/to/model/'+decodeURIComponent( derivativeUrn.split('Resource')[1]) //decode the URN and extract its path
}
Now let’s download the AEC data - query the manifest to locate its URN and it should look like:
{
"guid": "a4aac952-a3f4-031c-4113-b2d9ac2d0de6",
"type": "resource",
"role": "Autodesk.AEC.ModelData",
"urn": "urn:adsk.viewing:fs.file:dXJuOmFkc2sub2JqZWN0czpvcy5vYmplY3Q6c2IyMzMzMzMzL3Jldml0aG91c2UucnZ0/output/Resource/AECModelData.json",
"mime": "application/json",
"status": "success"
},
There are two options to load this data, one is to put AECModelData.json in the root path of your SVFs and call viewerDocument.downloadAecModelData() to let Viewer download it. Alternative assign it as JSON object to the viewable object like below:
const viewable = viewerDocument.search ...
viewable.data.aec_model_data = aecDataObject
Finally, be sure to load both the minimap and AECLevel extensions for the mini maps to work. And putting it all together:
const options = {
env: 'Local'
//...
}
const viewerConfig = { extensions:[
"Autodesk.AEC.LevelsExtension",
"Autodesk.AEC.Minimap3DExtension"
]}
const viewer = new Autodesk.Viewing.GuiViewer3D(container, viewerConfig);
Autodesk.Viewing.endpoint.getItemApi=(endpoint, derivativeUrn, api)=>{
return '/path/to/model/'+decodeURIComponent( derivativeUrn.split('Resource')[1])
}
Autodesk.Viewing.Initializer(options, () => {
const viewerDocument = new Autodesk.Viewing.Document(manifestJsonObject)
viewerDocument. downloadAecModelData()
viewer.start()
viewer.loadDocumentNode(viewerDocument, geometry, options)
})